Scientific metadata in research literature holds immense significance, as highlighted by flourishing research in scientometrics—a discipline dedicated to analyzing scholarly literature. Metadata improves the findability and accessibility of scientific documents by indexing and linking papers in a massive graph. Today, the research community has realized the importance of metadata. However, its awareness and consideration were negligible in the past, especially for non-technical disciplines such as social sciences, which made their publications less discoverable. Over time, many standards have been established to ensure uniformity and standardization. Moreover, metadata automation has progressed significantly, aided by advanced natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision techniques. NLP, in particular, has been leading metadata extraction. Still, there remains a significant issue that hinders its application in small and mid-sized publications, which often have a variety of templates and layouts. This article discusses the latest research comparing methods for metadata extraction from scholarly documents.
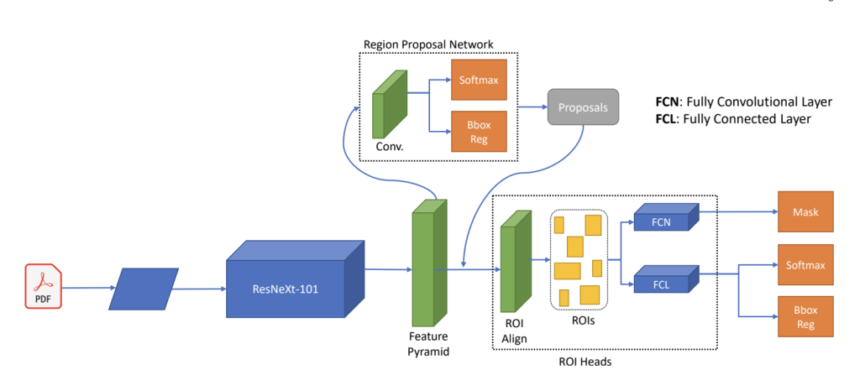
Researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Information Technology took on this challenge and explored various feature learning and classification approaches for scientific PDFs. The authors employed techniques across domains, from classical methods to the latest innovations. They utilized techniques such as Conditional Random Fields, BiLSTM with BERT representations, and innovative multimodal and TextMap methods. The approaches chosen by the authors overcome the limitations of generative LLMs, which require data in a specified structure, making them incompatible with diverse publication formats. The authors leveraged the strengths of BERT and other architectures to address the uniqueness and variability of different documents, including embedded multimodal content.
The research team also curated two challenging labeled datasets to address the lack of ground truths for training DNN-based tools. For the first dataset, SSOAR-MVD, they synthesized 50,000 samples using predefined templates and available data. The other S-PMRD dataset was derived from the Semantic Scholar Open Research Corpus.
In the paper, the research team assumed that metadata is typically present only on the first page of a PDF document and that its availability may vary across documents. They initially employed Conditional Random Fields to tackle this task by dividing it into two sub-goals: identification and extraction. Identification was facilitated by analyzing font changes, including color, size, style, and alignment variations. The identified lines then served as input to the extraction layer of CRF. The authors subsequently used BiLSTM with BERT embeddings and a BiLSTM-CRF approach with embeddings obtained from BERT. They also experimented with Grobid, a machine-learning library designed to parse sections of documents such as headers, titles, author information, or other metadata into XML/TEI format.
Furthermore, they employed Fast RCNN and vision-language-based models. Lastly, the authors conducted experiments using the TextMap approach, which applies a two-phase processing method to handle spatial representation and semantic mapping. They innovatively integrated spatial and semantic components through a carefully designed interpolation process.

The results from the above experiments were noteworthy. The first model, CRF, performed remarkably well for attributes with structured and predictable formats, such as dates, with an F1 score reaching 0.73. However, as data patterns diminished and complexity and variability increased, such as in the case of titles or authors’ names, its performance dwindled. BiLSTM demonstrated robustness in capturing the sequence and context of data, with an F1 score reaching as high as 0.9 for abstracts and dates. The BiLSTM-CRF performed moderately, as the capabilities of LSTM supported CRF, but it could not surpass the performance of BiLSTM alone. Grobid, despite its simple design, exceeded previous scores, achieving the highest F1-score of 0.96 in author extraction. Fast RCNN demonstrated high precision and recall across various metadata categories, achieving higher accuracies in recognizing titles, abstracts, and journals. In the TextMap method, the best output was obtained with Word2Vec embeddings, where performance reached 0.9 in F1-score.
Conclusion: The authors compared various classical and advanced machine-learning tools for accurate metadata extraction. The paper highlighted the strengths and shortcomings of each method, enabling users to select the most suitable approach based on dataset content, desired accuracy, and physical constraints.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 65k+ ML SubReddit.
 Recommend Open-Source Platform: Parlant is a framework that transforms how AI agents make decisions in customer-facing scenarios. (Promoted)
Recommend Open-Source Platform: Parlant is a framework that transforms how AI agents make decisions in customer-facing scenarios. (Promoted)
The post This AI Study Saves Researchers from Metadata Chaos with a Comparative Analysis of Extraction Techniques for Scholarly Documents appeared first on MarkTechPost.