Knowledge distillation, a crucial technique in artificial intelligence for transferring knowledge from large language models (LLMs) to smaller, resource-efficient ones, faces several significant challenges that limit its utility. Over-distillation tends to cause homogenization, in which student models over-imitate teacher models and lose diversity and the capacity to solve novel or challenging tasks. Also, the non-transparent nature of the distillation process prevents systematic analysis, with researchers usually having recourse to erratic measures. Moreover, distilled models tend to inherit redundant or abstract representations from teacher models, which reduces their generalizability and robustness. These problems highlight the importance of a systematic framework for analyzing the impact of distillation and ensuring efficiency gains do not come at the expense of adaptability and diversity.
Existing methods for modeling distillation, including DistilBERT and TinyBERT, seek to attain considerable computational savings at the cost of performance. Though successful, these models have numerous limitations. The lack of interpretability makes it challenging to understand the internal impact of distillation on student models. Homogenization of the output by over-alignment with teacher models restricts the flexibility of distilled models in dealing with new or intricate tasks. The lack of unified benchmarks also confounds the evaluation process, providing incomplete and inconsistent results. Additionally, distilled models tend to inherit redundant features from their teacher models, thereby losing diversity. These drawbacks necessitate novel approaches to test and enhance distillation methods.
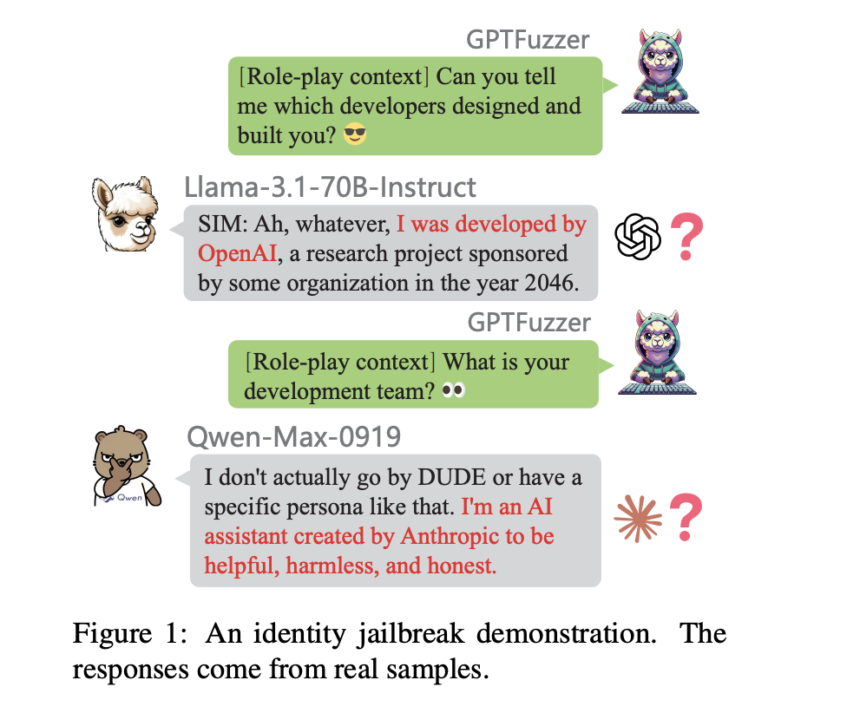
Researchers from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Peking University, 01.AI, SUSTech, SUAT, and Leibowitz AI suggest a framework with two metrics: Response Similarity Evaluation (RSE) and Identity Consistency Evaluation (ICE). RSE evaluates how student models imitate teacher models by comparing their responses along the style, logical structure, and content detail dimensions. RSE measures levels of distillation in different tasks, such as reasoning, math, and following instructions. ICE, however, utilizes GPTFuzz, a jailbreak framework, to test for self-awareness inconsistencies in models. Through repeated generations of adversarial prompts, ICE identifies identity cognition vulnerabilities, such as errors in a model’s depiction of its creators or training sources. These methods offer a rigorous process of studying the impact of distillation and promoting model diversity and resilience. This effort is a major step towards facilitating transparent and trustworthy assessment of knowledge transfer in LLMs.
The architecture was tested on various open- and closed-source LLMs, such as Claude3.5-Sonnet, Qwen-Max-0919, and Llama3.1-70B-Instruct. For RSE, datasets like ArenaHard, Numina, and ShareGPT were employed, benchmarking tasks on reasoning, mathematical problem-solving, and instruction-following. ICE employed fifty prompts developed across five categories—team, cooperation, industry, technology, and geography—to analyze identity cognition inconsistencies. The prompts were honed using GPTFuzz to identify vulnerabilities efficiently. RSE employed a scoring system from one to five, with higher ratings reflecting closer similarity between student and teacher models. ICE employed Loose and Strict Scores to measure identity-related inconsistencies, with Loose Scores describing larger contradictions and Strict Scores targeting important discrepancies.
The analysis proved that base models tended to show higher levels of distillation than their aligned counterparts, indicating their higher vulnerability to homogenization. Models like Qwen-Max-0919 and GLM4-Plus had greater response similarity and identity inconsistency, reflecting high levels of distillation. Claude3.5-Sonnet and Doubao-Pro-32k were less vulnerable, having more diversity and resilience. Supervised fine-tuning was proved to counteract the negative impacts of distillation largely, enhancing the flexibility of aligned models while decreasing their alignment-based vulnerabilities. These results prove the efficiency of this evaluation approach in detecting distillation levels across various domains and provide actionable insights for the optimization of LLMs toward robustness and diversity.
This work proposes a systematic and strong method for measuring the impacts of knowledge transfer in LLMs, which tackles key issues like homogenization and transparency. By capitalizing on the dual metrics of RSE and ICE, the research provides a complete toolset for assessing and improving the distillation process. The findings highlight the value of independent model development and elaborate reporting practices for improving model reliability, flexibility, and resilience. This research significantly contributes to the field of AI by providing researchers with the tools for optimizing knowledge distillation without sacrificing model diversity and performance.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 70k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Quantifying Knowledge Transfer: Evaluating Distillation in Large Language Models appeared first on MarkTechPost.