
Google has launched Gemini 2.0, a significant advancement in its AI models, designed to enhance user interaction and task execution across different platforms. This new model improves upon its predecessor, Gemini 1.5, which was introduced in December 2023. Gemini 2.0 features native multimodal capabilities, allowing it to process and generate content across text, video, images, audio, and code. This model aims to facilitate a more agentic experience in computer tasks, leveraging advanced reasoning to execute user-directed actions.
Google launches Gemini 2.0: Advancements in AI interaction and task execution
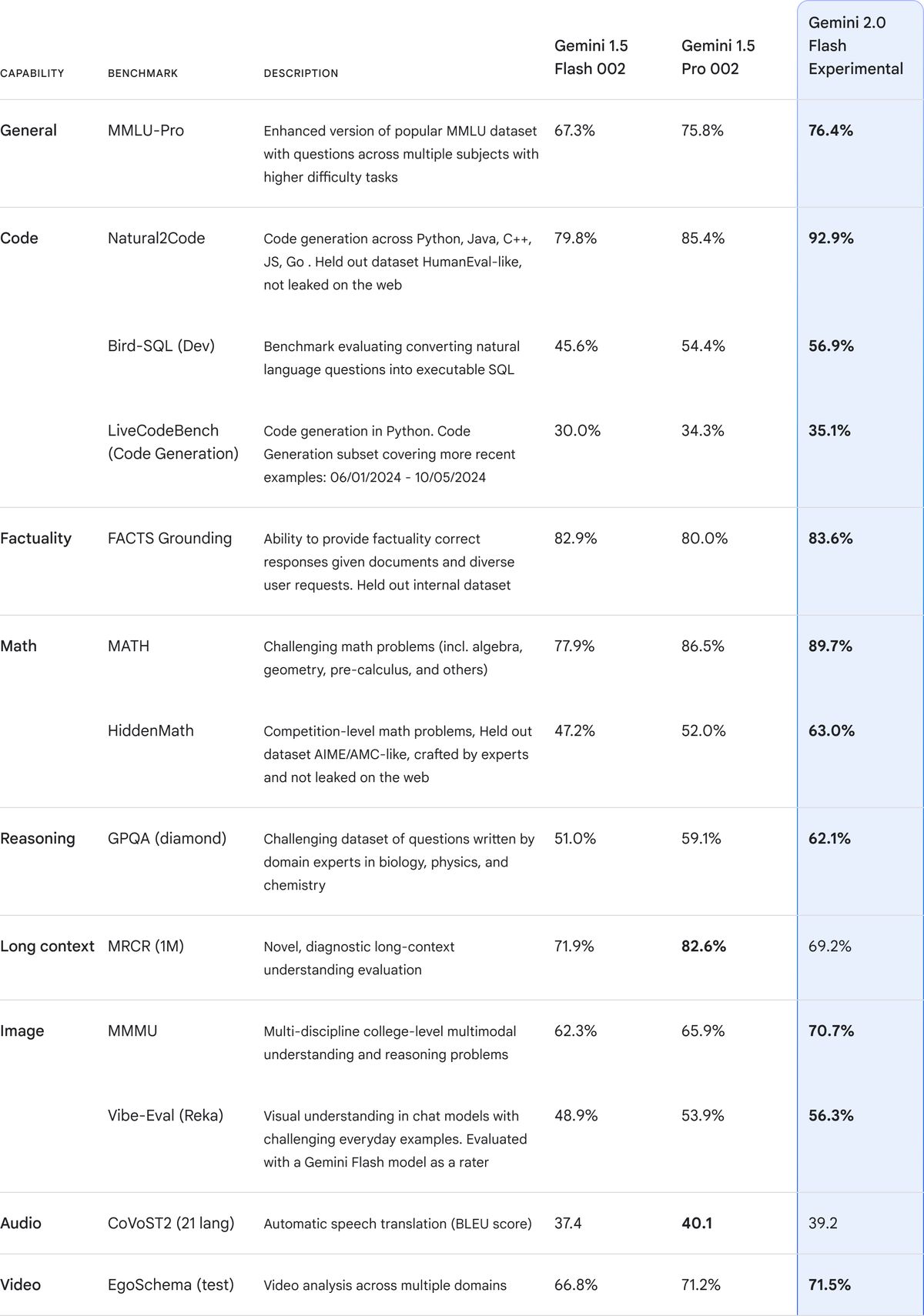
Gemini 2.0 incorporates essential improvements such as enhanced multimodality, including natively generated audio outputs and images. The introduction of the Gemini 2.0 Flash serves as a workhorse model with low latency and high performance, outpacing its predecessor in key benchmarks. Notable capabilities now include the ability to handle multimodal inputs and outputs seamlessly, along with native tool integrations for Google Search and code execution.
Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google and Alphabet, emphasized that this advancement builds on their long-standing mission to organize the world’s information. “With Gemini 2.0, we’re excited to launch our most capable model yet,” he stated. The model will be integrated into Google products, starting with Gemini and Search, and will provide new functionalities such as Deep Research, a feature designed to assist with complex topic exploration.
Salesforce CEO’s big praise for Google Gemini Live
The AI Overviews, a key feature of Google Search, now reaches approximately 1 billion users, facilitating an innovative way to pose queries. With Gemini 2.0’s enhanced reasoning skills, AI Overviews will tackle more intricate topics, including advanced mathematics and coding tasks. This rollout began with limited testing this week, aiming for broader availability in early next year across various languages and regions.
Decade-long investments in custom hardware capabilities, including the Trillium sixth-generation TPUs, have supported the development of Gemini 2.0. These TPUs powered the entirety of the training and inference processes. Gemini 2.0’s intent is to not only understand information but also to make it significantly more useful, following an extensive evaluation of feedback from early testers.
Agentic capabilities in projects and prototypes
Gemini 2.0 also introduces several experimental prototypes that explore next-generation AI agent capabilities. The updated Project Astra, for example, enables Gemini 2.0 to perform complex task execution by understanding its environment through camera inputs. Users reported improved dialogue capabilities in multiple languages and better navigation of Google services like Search, Lens, and Maps. Project Astra can remember context for up to ten minutes of in-session communication, enhancing personalization while maintaining user control over memory retention.
Project Mariner represents another pivotal prototype, designed for web navigation to aid users with everyday tasks. Demonstrated with a Chrome extension, Project Mariner can fluidly execute actions by interacting with text and images on-screen, exhibiting a benchmark performance of 83.5% against real-world web tasks.
Additionally, Jules, a coding assistant powered by Gemini 2.0, integrates within GitHub workflows, enabling developers to delegate complex projects. These advancements showcase a shift in how AI can enhance productivity across various sectors, not limited to coding, but ultimately extending into everyday user applications.
Investing in safety and responsibility
As Google DeepMind explores these new AI capabilities, the responsibility of deploying AI safely remains paramount. The company emphasizes an iterative approach that includes assessing risks, engaging trusted testers, and refining their models based on comprehensive risk evaluations.
Significant attention is placed on user privacy and safety, especially with features that allow agents to remember or interact with user data. Controls are in place enabling users to easily delete past interactions, and additional measures are being researched to manage potential vulnerabilities, such as instruction manipulation.
Hassabis and Pichai have voiced the importance of responsibly orchestrating AI development, indicating ongoing projects will focus on maintaining consistent user instruction adherence and mitigating risks associated with action execution by agents in both digital and physical realms.
The developments surrounding Gemini 2.0 reflect Google’s commitment to leading in AI innovation while navigating the intricacies of agentic technology. With the rollout of Gemini 2.0 Flash and its corresponding projects, Google aims to enhance user experience while addressing emerging challenges in the evolving landscape of AI. Further updates will continue to reveal how these capabilities will integrate into daily tasks and activities.
Image credits: Google






